Doctors. There never seems to be enough of them.
If you’ve been to a hospital recently, you’ve probably noticed that every member of staff appears to be rushed off their feet. The reason for this is simple: there is a worldwide shortage of healthcare professionals, which is having a direct impact on patients.
Driven by factors such as aging populations, the growing burden of chronic diseases, and inadequate training capacity, the World Health Organization estimates a global shortfall of over 4.3 million physicians, nurses, and other health professionals. Worryingly, this deficit is projected to rise to 12.9 million by 2035.
To counter this shortage, robots in healthcare are being developed to reduce the burden on clinicians while improving efficiency, enhancing the patient experience, and lowering overall costs.
Why Traditional Medical Robots Fall Short
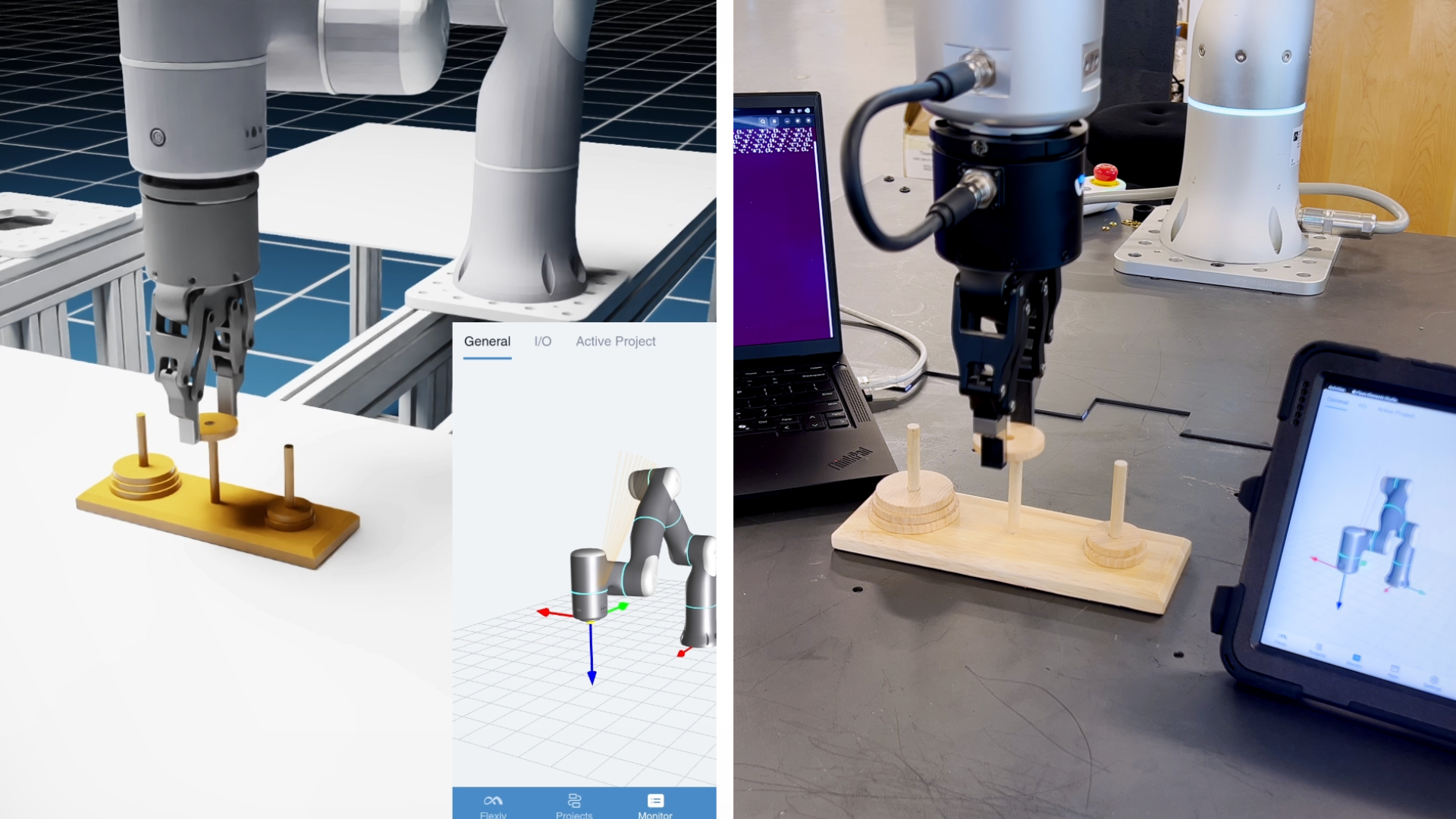
For medical robots to truly assist healthcare professionals, they must be easy to use, safe, and precise.
Unfortunately, many traditional types of healthcare robots often fail in these critical areas:
-
Prohibitive Costs
Traditional medical robots are extremely costly. For example, one of the world’s most popular systems, Intuitive Surgical’s da Vinci Surgical System, costs between $0.8–2.5 million USD.
-
Insufficient Responsiveness
Existing robots used in medical applications are unable to react autonomously. Patient movement or external interference can easily disrupt their accuracy and stability, potentially leading to unintended consequences.
-
Operational Complexity
Current medical robots often serve as assistive equipment, requiring operators to master both their routine operation and emergency handling. Training can take weeks for even basic use, while redeployment or retasking consumes additional time and resources.
-
Lack of "Sensitivity"
Most traditional robots used in medical settings are controlled through teleoperation. Without fine force control, these systems cannot provide the operator with accurate tactile feedback. As a result, surgeons must rely entirely on visual cues to determine what they are interacting with, significantly increasing the complexity and risk of procedures.
Providing a Sense of Touch
The Hippocratic Oath states that a doctor should first "do no harm". We believe that robots must abide by this same rule, and to achieve this, robots need tactile awareness of their environment.
Imagine not being able to feel when a bottle cap is fully seated, or failing to notice if your hand slips while writing. Without tactile awareness, small errors become invisible and inevitable. That is why Flexiv Rizon adaptive robots are designed to bridge this gap.
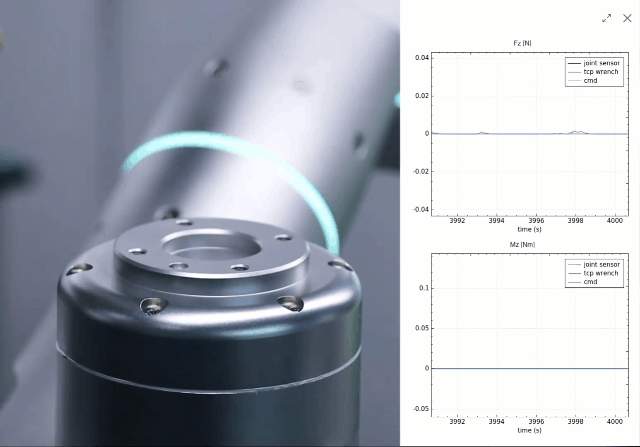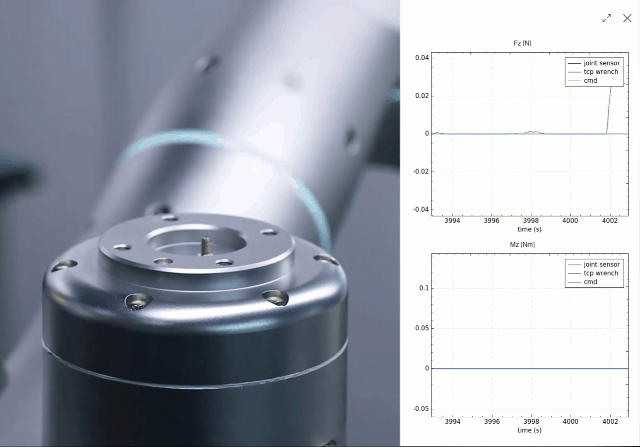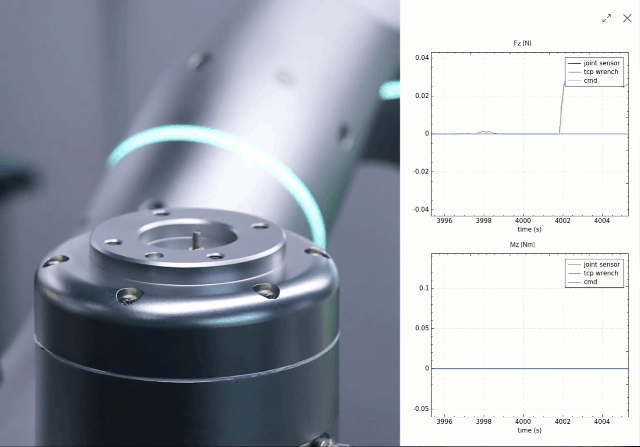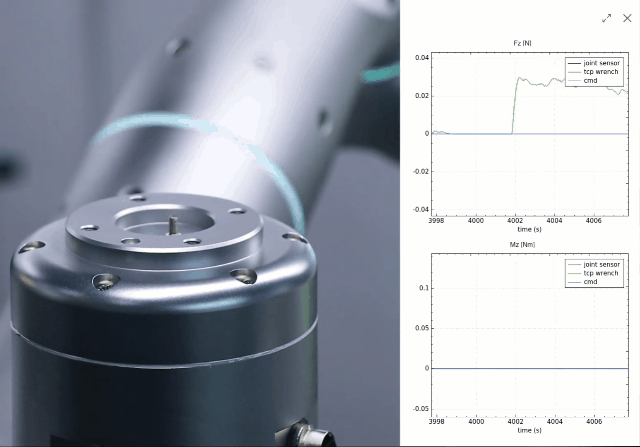
By integrating proprietary force/torque sensing, a novel joint design, low-level force control, and whole-body force sensitivity, Rizon robots possess ultra-precise force perception. This allows the robot to replicate the tactile intelligence of human manipulation, ensuring delicate, precise, and safe interactions.
Medical-grade Safety Architecture
In healthcare, safety isn't a feature. It's a requirement.
Flexiv’s Rizon adaptive robots incorporate a dual-channel redundant architecture and a torque-based control framework that meets or exceeds multiple international safety standards, including ISO-13849, PL=d, ISO-10218, ISO/TS-15006, and UL-1740.

After receiving CE and ETL certification in 2022, Rizon achieved IEC 60601 certification in 2023, ensuring intrinsic safety for patients and devices during contact-intensive procedures. Flexiv’s safety-centric functions include:
- Instantaneous force monitoring triggers an emergency stop upon detection of a collision or excessive force.
- Virtual wall boundaries to prevent dangerous actions or unintended contact.
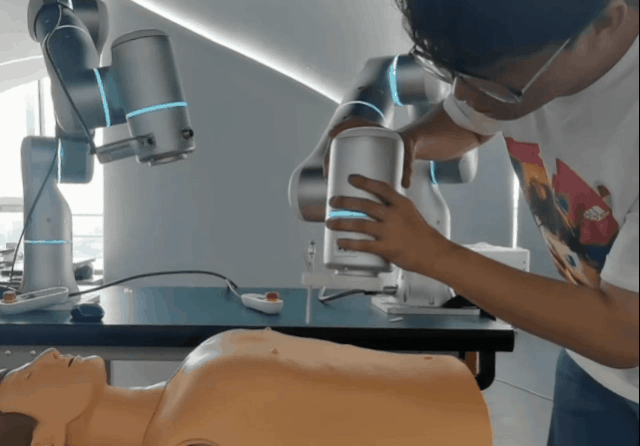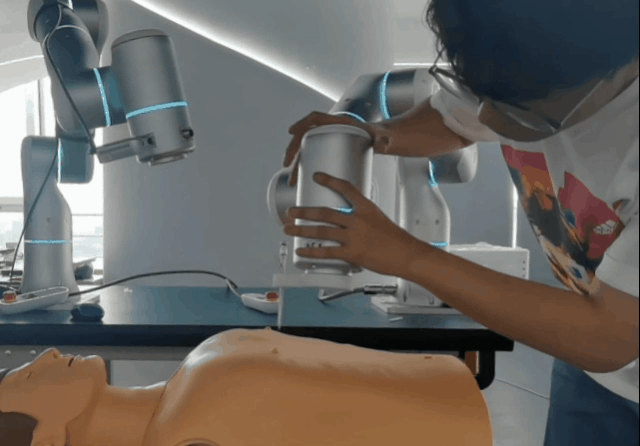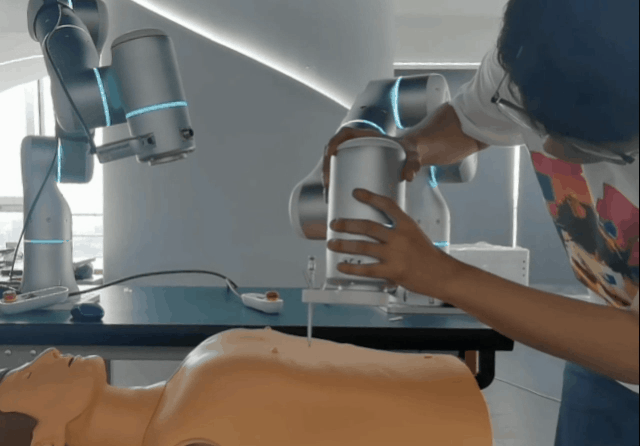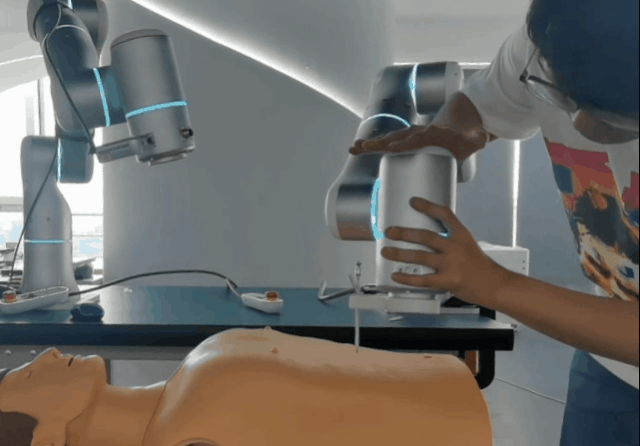
- Dynamic impact reactivity enables the robot to absorb shocks and prevent damage to itself or others.
Intuitive and Accessible Operation
For medical robots to be widely adopted, they must be intuitive. Flexiv’s Freedrive function allows clinicians to effortlessly guide the robot’s end-effector as if it were floating, simplifying teaching and simulation. When paired with the Flexiv Elements drag-and-drop programming system, applications can be created in hours rather than days.
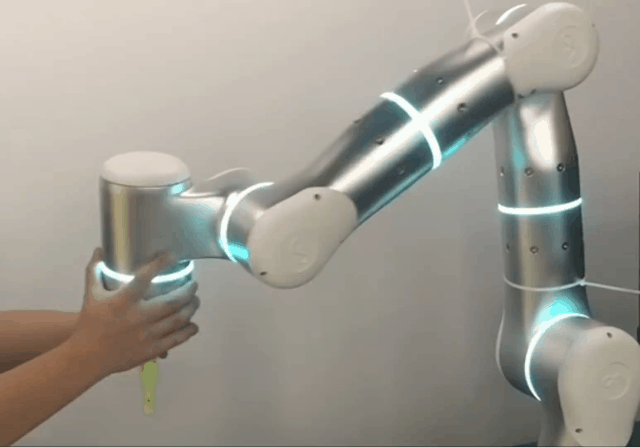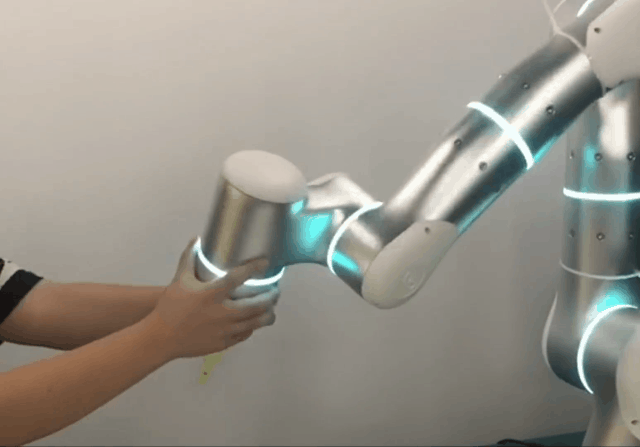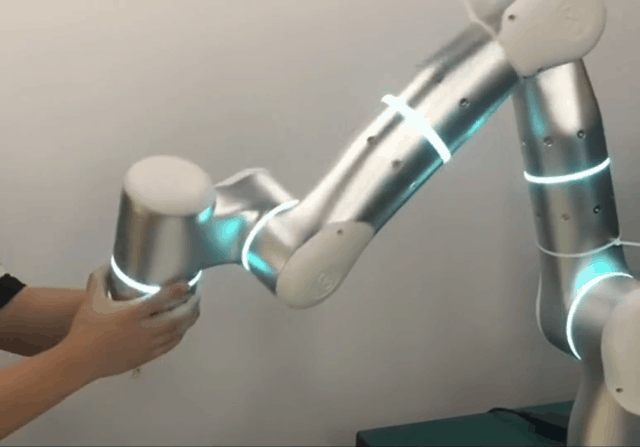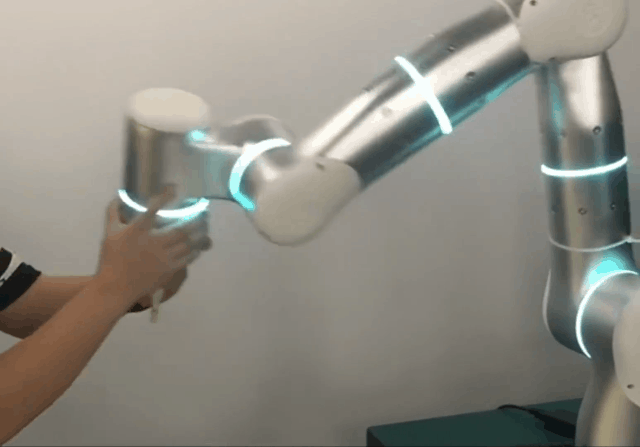
For advanced users, Flexiv also provides the Robot Development Kit. With this, programmers can create highly customized applications in C++ or Python.
It’s this adaptability that allows Flexiv to tackle the unique needs of every patient and clinician.
Expanding Medical Applications
In collaboration with specialists and consultants, Flexiv is broadening the scope of what a robot in healthcare can achieve. Mature use cases now include:
Ultrasound Diagnostics
Massage Therapy
Laboratory Automation
When providing therapeutic and chiropractic massage, Flexiv’s robots can replicate the exact movements of expert practitioners to deliver Tui Na, pain management, and sports rehabilitation.
The same principles of replication are directly applicable to delicate procedures such as cosmetic interventions, needle-free injections, and specimen collection.
Through partnerships with experts, Flexiv has already delivered innovative medical world firsts.
One notable case was with the Stanford Robotics Center, where Flexiv demonstrated Magnetic Milli-Spinner Vascular Therapy, in which a Rizon 4 robot guided micro-devices through blood vessels to deliver targeted treatment.
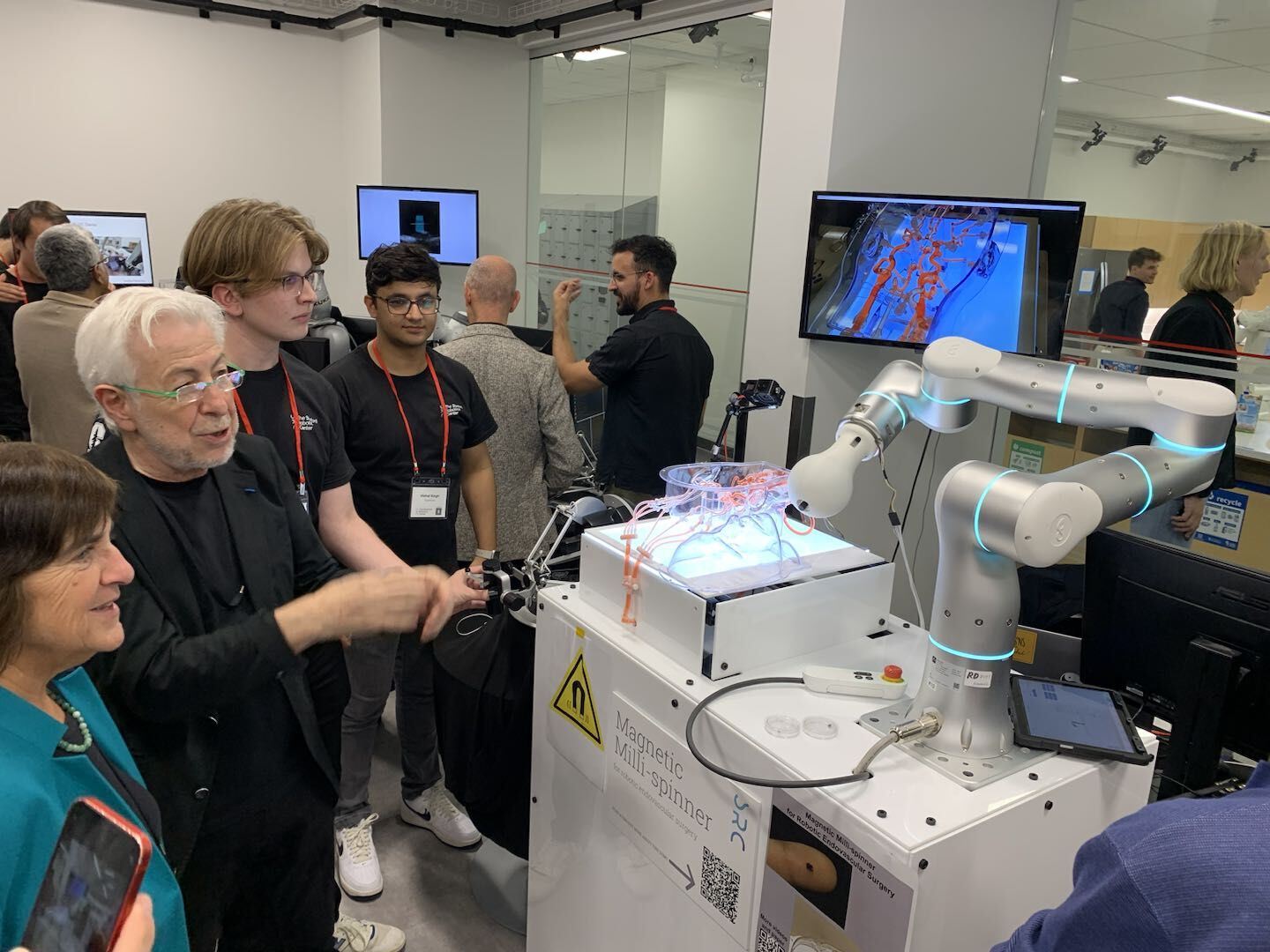

Creating ground-breaking applications is at the core of Flexiv, and that’s why we support surgical-robot OEMs. Currently, several projects have advanced clinical trials, among which include treatments for stroke and orthopedic surgery.
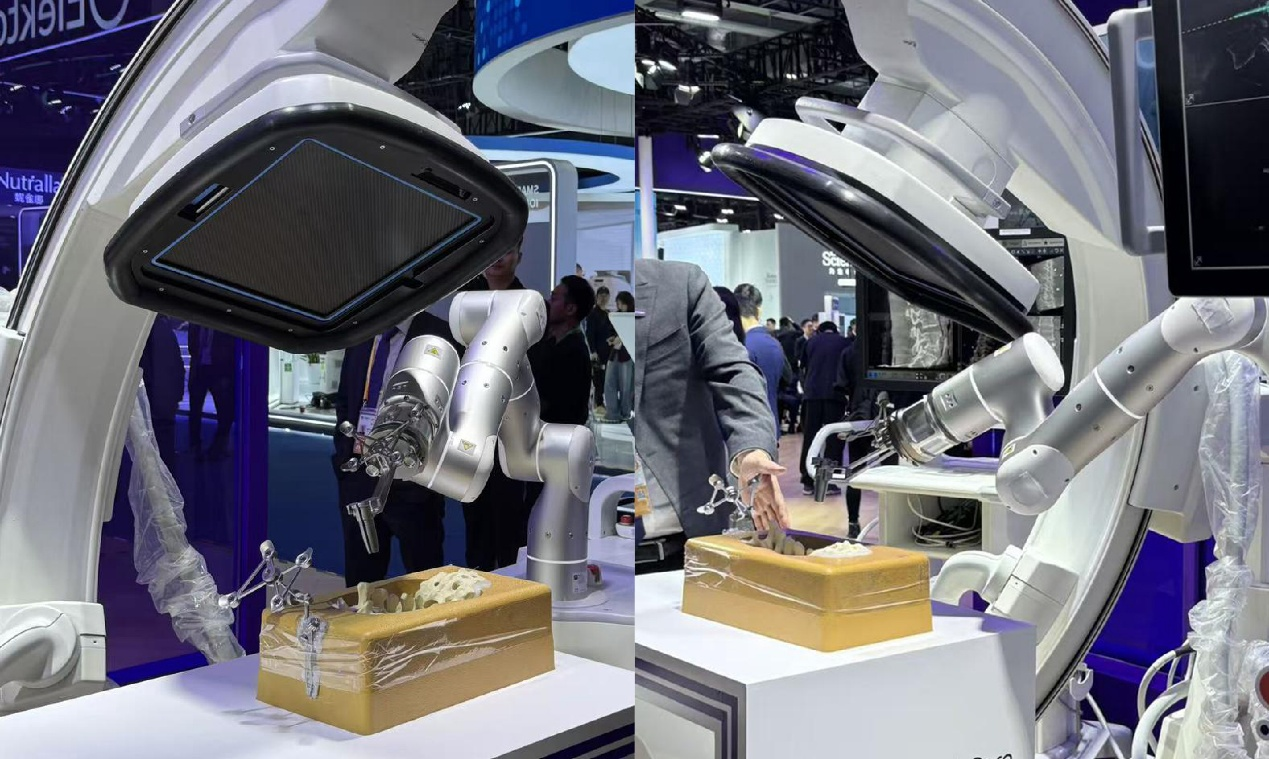

The Future of Healthcare
Healthcare applications require truly specialized solutions, and that’s why Flexiv is working in close cooperation with many healthcare professionals, to make human-robot interactions more than just teleoperated.
While full autonomy remains a future goal, we’re making significant progress in enhancing robotic capabilities in healthcare settings through integrating AI and advanced sensor technologies.
While we’re not there yet, we look forward to the day when healthcare is democratized, and prohibitive barriers of cost are removed.





