In the ever-evolving field of robotics, understanding the distinctions between different types of robots is crucial for selecting the right system for your application. Two primary categories of robots are serial and parallel robots. This article delves into the differences between these two types, their applications, and examples to help you make an informed decision.
Introduction to Serial and Parallel Robots in Robotics
Serial robots, the most common type of robotic arms used across various industries, consist of a series of joints and links connected end-to-end, forming a chain-like structure. Each joint in a serial robot adds a degree of freedom, enabling complex and flexible movements.
One of the key advantages of serial robots is their extensive reach and ability to navigate around obstacles. This makes them ideal for tasks that require a high degree of maneuverability, such as assembly, welding, polishing and painting. However, the sequential nature of their joints can sometimes lead to issues with speed and stability, especially when dealing with heavy loads.
Parallel robots, feature a different structural design compared to serial robots. In a parallel robot, multiple arms (or legs) connect a single platform to a fixed base. This configuration provides several advantages, including increased rigidity, better motion control, and load-bearing capacity.
Due to these characteristics, parallel robots are commonly used in applications that demand high efficiency and stability.
Machining and Manufacturing: Parallel robots are often employed in CNC machining and 3D printing due to their ability to maintain precise positioning and handle heavy loads.
Pick and Place Operations: Parallel robots excel in high-speed pick and place operations, making them suitable for packaging, sorting, and assembly lines.
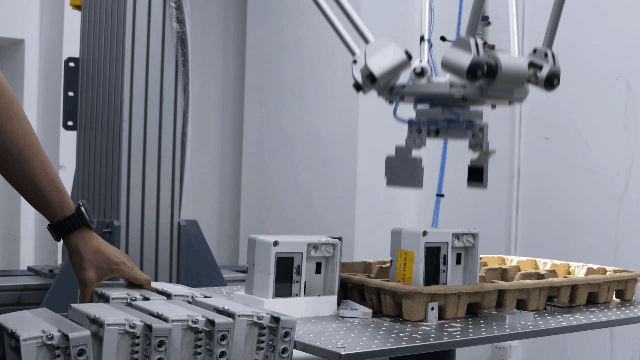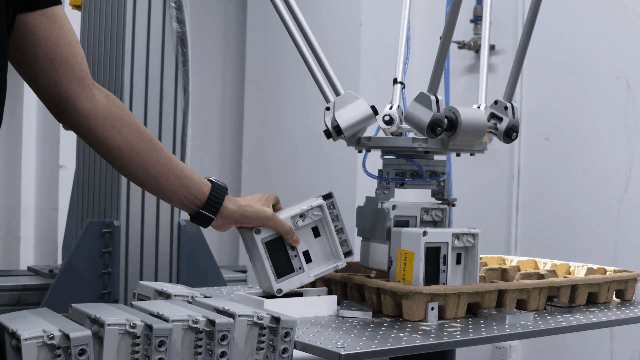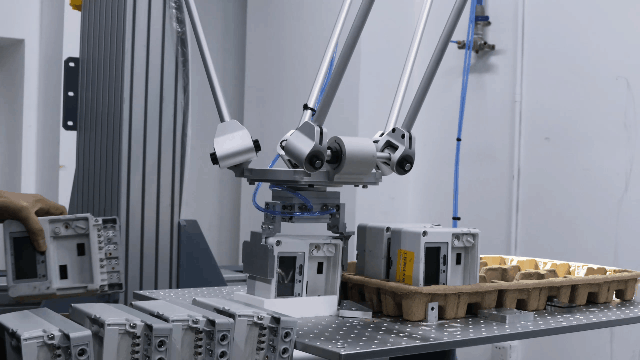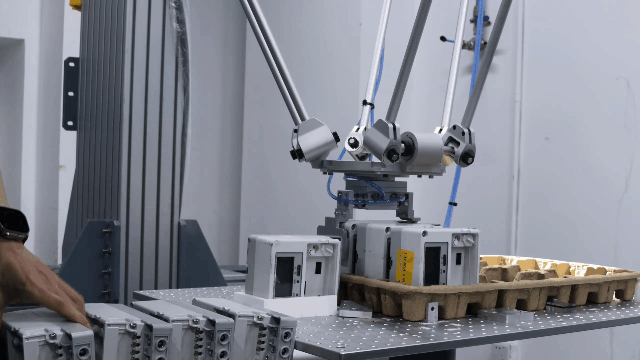
Examples of Parallel robots
To better understand the practical applications of parallel robots, let’s explore some notable examples:
Delta Robots: Delta robots are a type of parallel robot known for their high-speed and precise movements. They are widely used in the food and pharmaceutical industries for tasks such as packaging and sorting.
Stewart Platforms: Stewart platforms, also known as hexapods, are six-legged parallel robots used in applications requiring six degrees of freedom. They are commonly used in flight simulators, motion platforms, and precision machining.
Flexiv Moonlight: Flexiv Moonlight series is an excellent example of a parallel robot robot designed for industrial applications. With its advanced control algorithms and high precision, Moonlight robot is ideal for tasks such as assembly, inspection, and material handling. Additionally, the Moonlight robot features advanced force control capabilities, allowing it to detect and adapt to varying force requirements in real-time. This ensures precise handling of delicate or complex tasks, such as assembling sensitive components or operating in environments with unpredictable forces. The integration of force control technology not only enhances accuracy but also reduces the risk of damage to materials, making it a reliable solution for high-precision industrial applications.
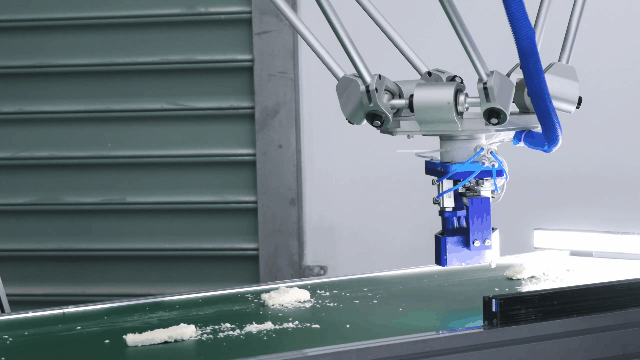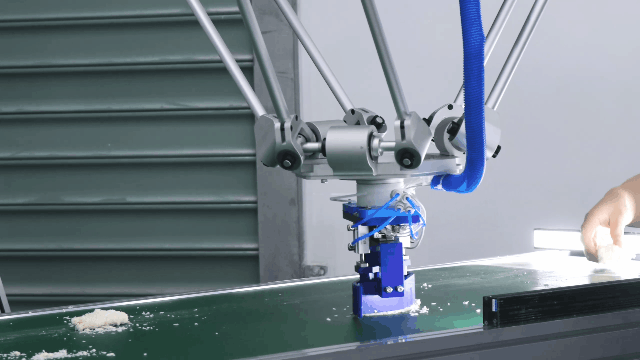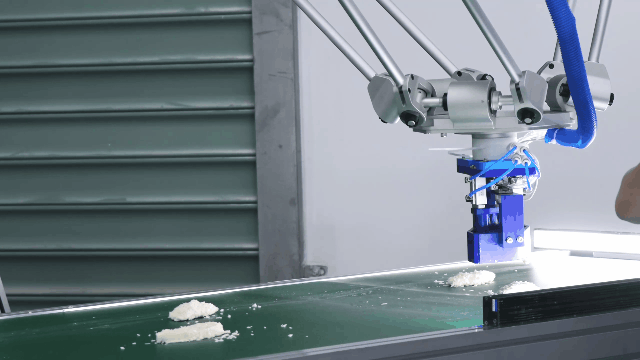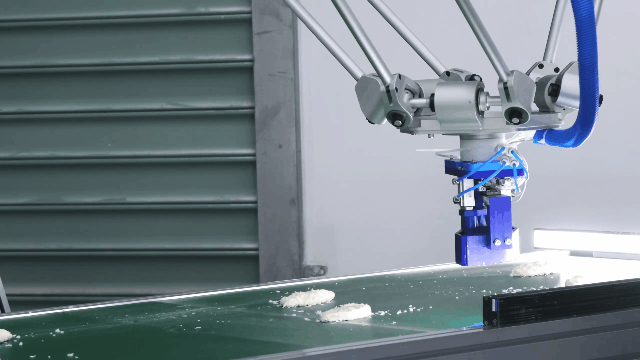
Flexiv Rizon Series: The Flexiv Rizon series is an exceptional example of a serial manipulator designed for versatile industrial applications. With its advanced force control and adaptive capabilities, the Rizon robot is ideal for tasks such as polishing, assembly, and inspection. The Rizon robot features cutting-edge force-sensing technology, allowing it to detect and adapt to varying force requirements in real-time. This ensures precise handling of delicate or complex tasks, such as polishing intricate surfaces or assembling components with tight tolerances. The integration of force control technology not only enhances accuracy but also enables the robot to work seamlessly in dynamic environments, making it a reliable solution for applications that require both flexibility and precision. Its unique combination of high adaptability and advanced control algorithms positions the Rizon series as a leader in modern robotics, catering to the evolving needs of industries worldwide.
Understanding the differences between parallel and serial robots is essential for selecting the right robotic system for your needs. Serial robots offer flexibility and reach, making them suitable for tasks requiring maneuverability. In contrast, parallel robots provide precision, stability, and load-bearing capacity, making them ideal for applications demanding high accuracy. By considering the specific requirements of your application, you can make an informed decision and leverage the strengths of each type of robot to achieve optimal results.





